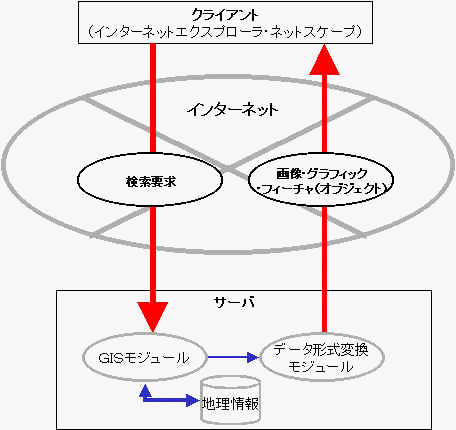
To understand population
characteristics in Malaysia, an Internet GIS(Web GIS or
Web-based GIS) was created that can analyze demographic
statistics, and its applicability was investigated in this paper.
This system would be available for foreign researchers,
administrators and business people who want geographical
information on Malaysia. Users can access a wide variety of
attribute data and political map data through the Internet. These
are linked on a network, allowing all types of thematic maps to
be compiled and statistical processing to be conducted. This
system creates choropleth maps that have the functions of "Zoom
In", "Zoom Out," graph displays,
attribute query, and basic spatial analysis, among other
features.
The purpose of this study
is to construct a Geographic Information System on the Internet
that has the capability to spatially analyze population
characteristics in developing countries (see Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Schematic
depiction of Internet GIS.
Digitization of
statistics, maps, etc., in developing countries is lagging that
in developed countries, and there is little opportunity to access
digital regional statistics and thematic maps from developing
countries. It is nearly impossible to get spatial data through
the Internet, and most geographic information is still obtainable
only through printed media. Therefore, Internet GIS would be an
invaluable resource for geographical research of developing
countries as it would allow anyone in the world to use a Web
browser to freely create statistical maps and conduct spatial
analysis.
Given this background,
this paper will examine the case of Malaysia. To understand the
demographics of the country, an Internet GIS was created
that can analyze demographic statistics, and its applicability
was investigated. This new program should be useful for persons
who are interested in the characteristics of Malaysian regions
and/or want geographical information on Malaysia, especially
foreign researchers, administrators and business people.
Three methods were
considered to bring Internet GIS to fruition: 1) processing done
mostly by the server, 2) processing done mostly by the user, and
3) processing split between server and user, according to the
capabilities of each. To create a highly utile system in which
the user can give frequent processing commands in the present
Internet GIS, method 2 was chosen since it allows relatively easy
interactive spatial analysis.
The author has opened an
experimental web page from his laboratory entitled "Internet
GIS for Historical Statistics" (http://giswin.geo.tsukuba.ac.jp/teacher/murayama/index-e.htm)
which provides the user with an understanding of the
socioeconomic structure of modern Japan, from the early Meiji Era
(ca. 1878) to the early Showa Era (ca. 1930). The present study
has improved on this experimental system by increasing processing
speed and giving it more functionality for spatial analysis in
order to create an Internet GIS for demographic statistics of
Malaysia.
It should be noted that
the map files are read by a modified version of Java Shapefile
Reader Ver. 1.0b, a freeware developed by the Geography
Department of Leeds University in the United Kingdom.
Various services using
Internet GIS have been provided to the world since the latter
half of the 1990s (Plewe, 1997). Recently it has become much
easier to use Java language, which works with any computer
operating system, spurring the development of Internet GIS.
The Geography Department
of the University of London is one of the leading institutions
involved with Internet GIS research. The Department has organized
the Great Britain Historical GIS Program to utilize Internet GIS
to analyze and process historical statistics of the UK. Their Web
page can be accessed at http://www.geog.qmw.ac.uk/hgis/
This British project
involves data from the late 1830s, when modern statistical data
were first collected, to the 1970s. Political (election) and
socioeconomic data were linked via computer to allow users to
easily compile statistical maps, then the system was made
accessible to Internet users worldwide.
In Japan as well, great
strides are being made in creating a practical Internet GIS. For
example, there is the "Map on Demand" developed
jointly by the DNP and Pasco corporations (http://www.map-ondemand.ne.jp/visitor/index.htm).
This system was designed for area marketing and is provided
through Java applets. If the user has a Web browser, he or she
does not need any special hardware or software. Using this
system, it is possible to create map displays and conduct
regional analyses on 1,447 statistical categories in the Japanese
census. The five types of areal units include two types of local
administrative districts (oaza, cho-cho), statistics for chikuchoson
divisions, and regional tertiary and quaternary grid statistics.
Users can freely choose the scale of map displays.
USER
REQUIREMENTS
Hardware
IBM-compatible PC (recommended)
Memory: At least 64 megabytes
Hard disk memory: At least 2 gigabytes
Windows 95/98/NT4.0
JDK 1.1.X or above
Netscape 4.0.6 or above, or
Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0.1 or above
Computer: Sun Workstation
OS: UNIX
HTTP: NCSA
Maps: Map file and associated data
Metadata: File locational information, names
of attribute data categories
The object of the present
research is Peninsular Malaysia. The data used here were taken
from the "Population and Housing Census of Malaysia"1)
compiled by the Department of Statistics Malaysia. Population
statistics from 1911 on were available for Peninsular Malaysia.2)
There was a total of 188
variables analyzed in the present study, representing the
statistical categories of sex, religion, school attendance,
citizenship, status in labour force, employment, occupation,
possession of household appliances, housing units, material of
outer walls, age of living quarters, occupancy, type of lighting,
type of toilet facility, total population, highest education
certificate, and hours worked (see Table 1). Regarding the
spatial scale, three different administrative units have been
used here: State, Administrative District, and Mukim (the
smallest unit). In Peninsular Malaysia there are 12 states
(including the federal territory of Kuala Lumpur), 81
administrative districts, and 844 mukims.
| Table
1 Items for Peninsular Malaysia, 1991. |
|
Category |
Item |
SEX |
Male |
|
Female |
RELIGION |
Islam |
|
Christianity |
|
Hinduism |
|
Buddhism |
|
Confucianism/Taoism |
|
Tribal/Folk |
|
Other |
|
No
Religion |
|
Unknown |
SCHOOL
ATTENDANCE |
Currently
Enrolled |
|
Completed
Schooling |
|
Unknown
(Currently/Completed) |
|
Never
Attended School |
|
Unknown |
CITIZENSHIP |
Malaysia |
|
Singapore |
|
Indonesia |
|
Philippines |
|
Thailand |
|
Brunei
Darussalam |
|
Other |
|
Unknown |
LABOUR
FORCE STATUS |
Employed
(At Work) |
|
Employed
(Not At Work) |
|
Unemployed
(Active) |
|
Unemployed
(Inactive) |
|
Outside
Labour Force |
|
Unknown |
EMPLOYMENT
STATUS |
Employer |
|
Employee |
|
Self-Employed |
|
Unpaid
Family Worker |
|
Unknown
Employment Status |
|
First-time
Job Seeker |
|
Other
Unemployed |
|
Outside
Labour Force |
|
Unknown
Labour Force Status |
OCCUPATION |
Professional,
Technical or Related Worker |
|
Administrative
or Managerial Worker |
|
Clerical
or Related Worker |
|
Sales
Worker |
|
Service
Worker |
|
Agricultural
worker |
|
Production
or Related Worker, Transport Equipment Operator and
Labourer, etc. |
|
Occupation
Inadequately Described |
|
Occupation
Unknown |
|
Unemployed |
|
Outside
Labour Force |
|
Unknown
Labour Force Status |
HOUSEHOLD
ITEMS |
1
Motorcar |
|
2
Motorcars |
|
3
or More Motorcars |
|
1
Motorcycle |
|
2
or More Motorcycles |
|
Bicycle |
|
Air-conditioner |
|
Refrigerator |
|
Washing
Machine |
|
Telephone |
|
Television |
|
Video |
|
Radio/Hi-Fi |
|
Boat
with Engine |
|
None
of the Items Listed |
|
Unknown |
HOUSING
UNITS |
Detached |
|
Semi-detached |
|
Terrace,
Row etc. |
|
Longhouse |
|
Flat/Apartment/Condominium |
|
Shophouse,
Office |
|
Room
(In-shophouse, Office, etc.) |
|
Improvised/Temporary
Hut, etc. |
|
Other |
MATERIAL OF
OUTER WALLS |
Brick |
|
Plank |
|
Brick
and Plank |
|
Other |
|
Unknown |
AGE OF
LIVING QUARTERS |
0
- 6 |
(years) |
7
- 11 |
|
12
- 16 |
|
17
- 21 |
|
22
- 26 |
|
27
- 31 |
|
32
- 36 |
|
37
- 41 |
|
42
and over |
|
Unknown |
OCCUPANCY |
Occupied |
|
Vacant |
TYPE OF
LIGHTING |
Electric
Lighting |
|
Pressure/Gas
Lamp |
|
Oil
Lamp |
|
Others |
TYPE OF
TOILET FACILITY |
Flush
System |
|
Pour
Flush |
|
Bucket |
|
Pit |
|
Enclosed
Space over Water |
|
Other |
TOTAL
POPULATION |
Total
Persons 10 - 14 Years |
|
Total
Persons 15 - 64 Years |
|
Total
Persons 65 Years & Over |
HIGHEST
CERTIFICATE |
None |
|
SRP/LCE |
|
SPM/MCE/SC/4
Thanawi |
|
SPVM/SPM(V)/MCVE |
|
STPM/HSC/STA |
|
Diploma/
Certificate |
|
Degree |
|
Unknown |
|
Filler |
HOURS
WORKED |
Less
Than 30 Hours |
(per week) |
30
Hours or More |
|
Unknown |
In addition to Peninsular
Malaysia, the present study also used data from Kuala Lumpur,
especially the very minute statistical districts to
construct the Internet GIS. The reason for this inclusion is that
since Kuala Lumpur is a major city of 1.23 million inhabitants
(1991 data), it was determined that users would have a very high
need for choropleth maps and spatial analysis of this area.3)
The statistical
categories for 1980 are shown in Table 2; for 1991, in Table 3.
| Table
2 Items for Kuala Lumpur, 1980. |
|
category |
Item |
AGE |
0-4 |
|
5-9 |
|
10-14 |
|
15-19 |
|
20-24 |
|
25-29 |
|
30-34 |
|
35-39 |
|
40-44 |
|
45-49 |
|
50-54 |
|
55-59 |
|
60-64 |
|
65+ |
SEX |
Male |
|
Female |
ETHNIC
GROUP |
Malay |
|
Chinese |
|
Indian |
|
Other |
OCCUPATION |
Professional |
|
Administrative |
|
Clerical
or Related Worker |
|
Sales
Worker |
|
Service
Worker |
|
Agricultural
Worker |
|
Production
or Related Worker |
|
Looking
for First Job |
|
Occupation
Inadequately Described |
|
Not
Stated |
|
Outside
Labour Force |
HOUSING
UNITS |
Detached |
|
Semi-Detached |
|
Terrace,
Row or Link |
|
Longhouse |
|
Flat/Apartment |
|
Room |
|
Makeshift/Improvised
Hut |
|
Other |
HOUSEHOLD |
Non
Private Household |
|
Private
Household |
| Table
3 Items for Kuala Lumpur, 1991. |
|
category |
Item |
AGE |
0-14 |
|
15-64 |
|
65
and Over |
SEX |
Male |
|
Female |
ETHNIC
GROUP |
Malay |
|
Other
Bumiputera |
|
Chinese |
|
Indian |
|
Other |
RELIGION |
Islam |
|
Christianity |
|
Hinduism |
|
Buddhism |
|
Confucianism/Taoism/Other
Traditional Chinese Religion |
|
Tribal/Folk
Religion |
|
Other |
|
No
Religion |
|
Religion
Unknown |
SCHOOL
ATTENDANCE |
Currently
Enrolled |
|
Completed
Schooling |
|
Unknown
(Currently/ Completed) |
|
Never
Attended School |
|
Attended
School (Unknown) |
MARITAL
STATUS |
Never
Married |
|
Married
|
|
Widowed
|
|
Divorced/
Permanently Separated |
CITIZENSHIP |
Malaysia |
|
Singapore |
|
Indonesia |
|
Philippines |
|
Thailand |
|
Brunei |
|
Other |
|
Unknown |
LABOUR
FORCE STATUS |
Employed
(At Work) |
|
Employed
(Not At Work) |
|
Unemployed
(Active) |
|
Unemployed
(Inactive) |
|
Outside
Labour Force |
|
Unknown |
EMPLOYMENT
STATUS |
Employer
|
|
Employee
|
|
Self-Employed |
|
Family
Worker |
|
Unknown
Employment Status |
|
Looking
for First Job |
|
Other
Unemployed |
|
Outside
Labour Force |
|
Labour
Force Status (Unknown) |
OCCUPATION |
Professional,
Technical or Related Worker |
|
Administrative
or Managerial Worker |
|
Clerical
or Related Worker |
|
Sales
Worker |
|
Service
Worker |
|
Agricultural
Worker |
|
Production
or Related Worker, Transport Equipment Operator and
Labourer, etc. |
|
Occupation
Inadequately Described |
|
Occupation
Unknown |
|
Unemployed
|
|
Outside
Labour Force |
|
Unknown
Labour Force Status |
HOUSEHOLD
ITEMS |
1
Motorcar |
|
2
Motorcars |
|
3
or More Motorcars |
|
1
Motorcycle |
|
2
Motorcycles |
|
Bicycle |
|
Air-Conditioner |
|
Refrigerator |
|
Washing-Machine |
|
Telephone |
|
Television |
|
Video |
|
Radio-Hi-Fi |
|
None
of Items Listed |
|
Unknown |
HOUSING
UNITS |
Detached |
|
Semi-
Detached |
|
Terrace,
Row or Link |
|
Longhouse |
|
Flat/
Apartment |
|
Shophouse,
Office |
|
in
Shophouse, Office |
|
Improvised/
Temporary |
|
Others |
MATERIAL OF
OUTER WALLS |
Brick |
|
Plank |
|
Brick
and Plank |
|
Other |
|
Unknown |
AGE OF
LIVING QUARTERS |
0
- 6 |
(Years) |
7
- 11 |
|
12-16 |
|
17-21 |
|
22-26 |
|
27-31 |
|
32-36 |
|
37-41 |
|
42
and Over |
|
Unknown |
OCCUPANCY |
Occupied |
|
Vacant |
SOURCE OF
DRINKING WATER |
Piped
Water Inside |
|
Piped
Water Outside |
|
Well |
|
Other |
TYPE OF
LIGHTING |
Electric
Lighting |
|
Pressure/Gas
Lamp |
|
Oil
Lamp |
|
Other |
TYPE OF
TOILET FACILITY |
Flush
System |
|
Pour
Flush |
|
Bucket
|
|
Pit
|
|
Enclosed
Space over Water |
|
Other |
SHARED/EXCLUSIVE |
Shared
Toilet |
|
Private
Toilet |
|
Shared
Unknown |
|
|
The above regional
statistics were compiled into a database in the form of a
geographical matrix and are stored on the server at the
University of Tsukuba. It should be noted that all values are
expressed as percentages of total values. For example, the value
for Male (under "Sex") in Table 1 is the proportion of
males to the entire population.
This system creates
choropleth maps that have the functions of "Zoom In",
"Zoom Out," graph displays, attribute query, and
basic spatial analysis, among other features. Users can access a
wide variety of attribute data and political map data through the
Internet. These are linked on a network, allowing all types of
choropleth maps to be compiled and statistical processing to be
conducted (see Fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Home
Page.
First, the user selects
the spatial unit to be analyzed, i.e., state, administrative
district, or mukim. Figures 3 and 4 show sample screens
for state and mukim, respectively.
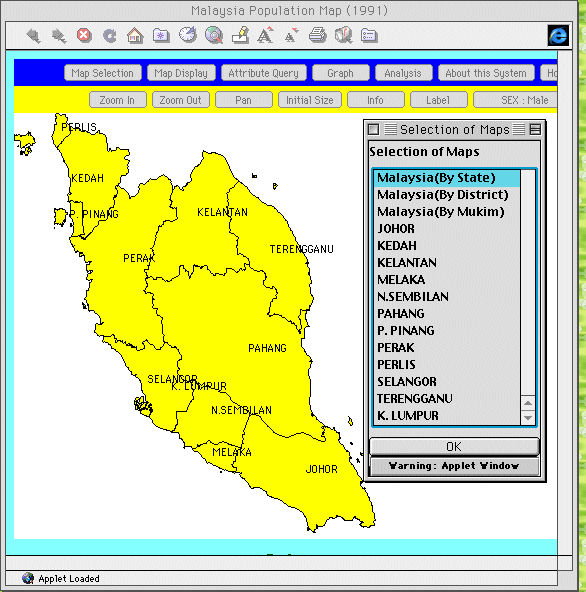
Fig. 3. Selection of
State unit.
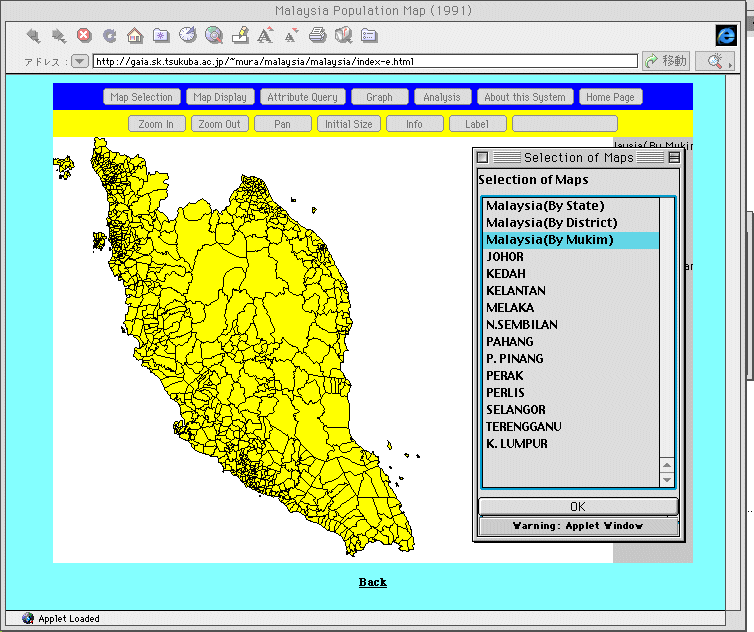
Fig. 4. Selection of
Mukim unit.
The user then selects a
blank map from the pull down menu to depict the attributes and
their distribution on the choropleth map. Depending on the needs
of the user, the legend can be divided into 2 to 7 hierarchical
levels, and changed at will.
These hierarchical levels
can be selected using three different modes: 1) "equal
size intervals", which make all hierarchical intervals
equal in size; 2) "equal number of features",
which makes the number of features the same in all levels; and 3)
"standard deviation", which shows mean attribute
values as 0 and variance as 1.
Figure 5 shows a sample
choropleth map in which the distribution of the male ratio
in Peninsular Malaysia in 1991 is shown with 7 hierarchical
levels in "equal size interval" mode. Figure 6
uses the same levels and mode to depict "Ethnic group:
Chinese ratio" for Kuala Lumpur for 1991.
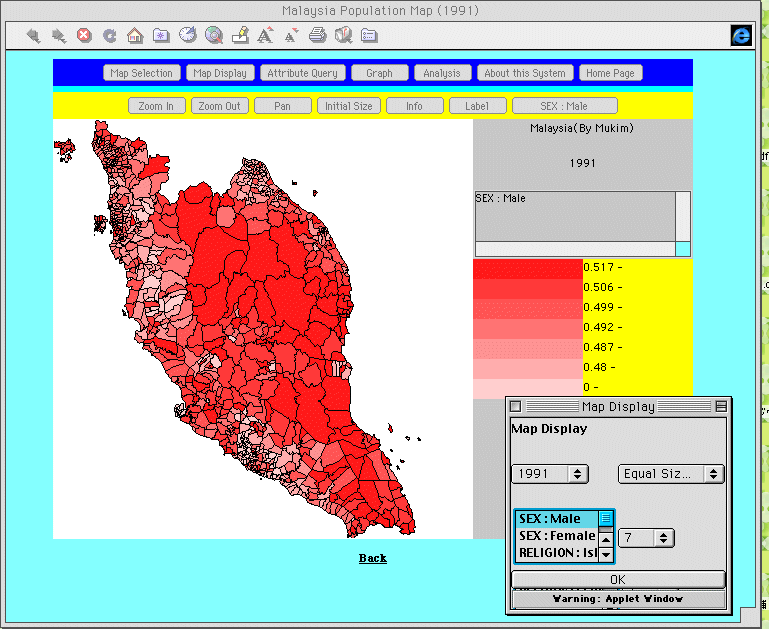
Fig. 5. Map display
of 1991 Male ratio in Peninsular Malaysia
based on equal size intervals.
@
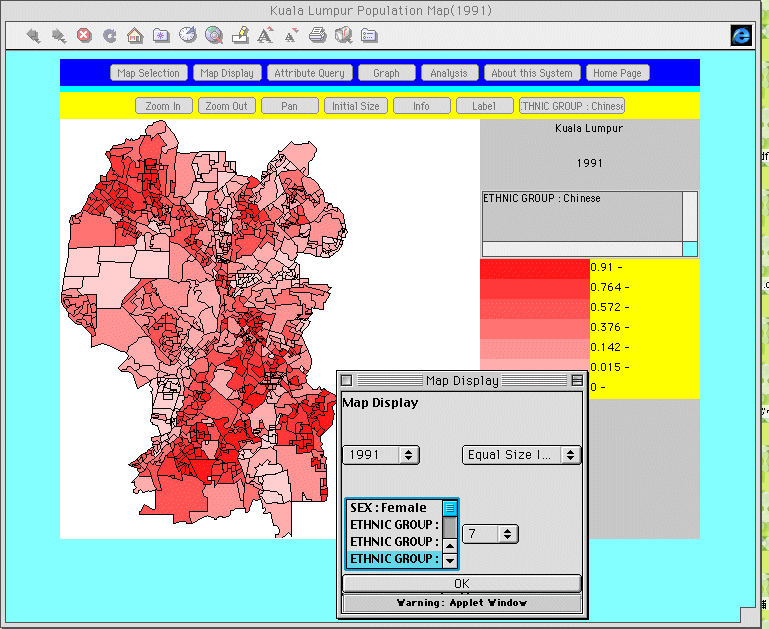
Fig. 6. Map display
of 1991 Chinese ratio in Kuala Lumpur based
on equal size intervals.
@
On the screen displaying the map, the user, simply by clicking the mouse on a region, can obtain information on it such as code number, attribute value, and place names.
@
Clicking the "Label Display" button on the tool bar will automatically display place names.
The enlarging and
reduction functions ("Zoom In" and "Zoom
Out") make it possible to change the scale of the map.
To enlarge an area, the user clicks the "Zoom In"
button on the tool bar, then designates the area to be enlarged
with the mouse. Thereupon, the mouse cursor will turn into a
"+" sign, and the designated area of the map will be
displayed on a larger scale. Figure 7 shows an example of an
enlarged section of a choropleth map for the Islam ratio
of the Selangor region.
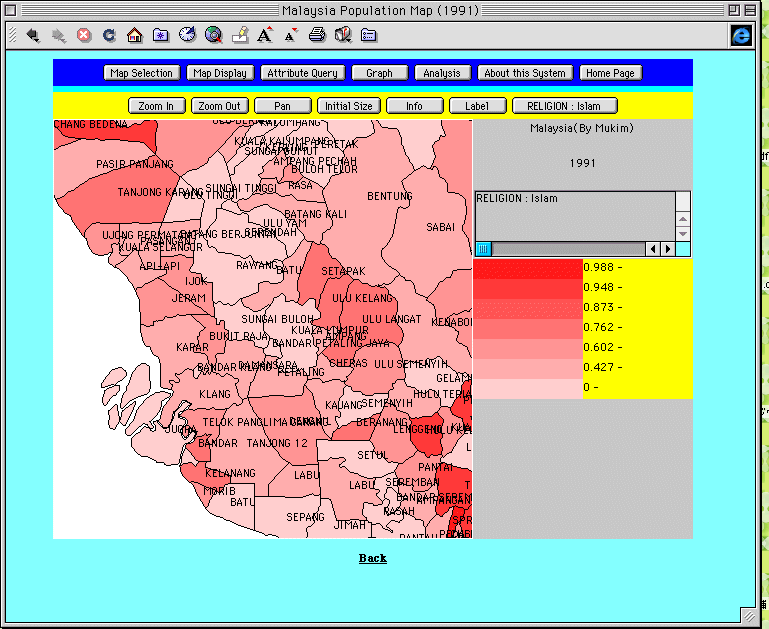
Fig. 7. Zoom In
function (Islam ratio in the Selangor
region, 1991).
To reduce the size of the
displayed area, the user clicks the "Zoom Out"
button on the tool bar. The mouse cursor will then turn into a
"+" sign, and the designated area of the map will be
displayed on a smaller scale.
By clicking the "Pan"
button, the user can freely move the position of the map on the
screen by holding down the mouse button, dragging the map to the
desired location, then releasing the mouse button.
Clicking the "Initial
Size" button at the top of the screen will return the
map to its original scale and position.
This is a function that
searches attribute values based on numerical parameters and
displays areas having those values on the map. For example, by
setting the population parameter as "10,000 or over",
regions of less than 10,000 population will not be displayed.
Figure 8 shows an example of regions at the mukim level
for Peninsular Malaysia in 1991 in which the Islamic ratio
(proportion of Moslems to entire population) is 0.6 (60%) or
greater.
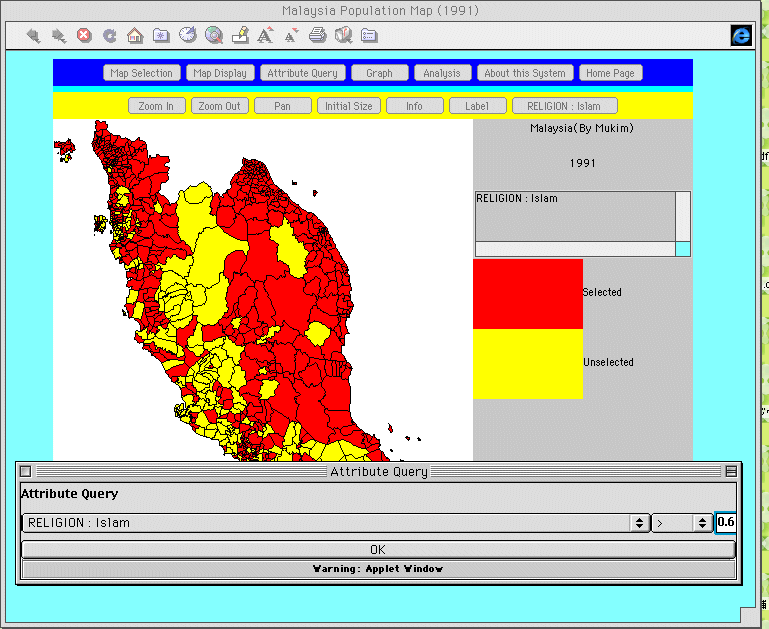
Fig. 8. Attribute
query function.
Graph display
By using this function,
the relation between two variables can be displayed as a
scattergram. Figure 9 shows Islam ratio on the x-axis, and
agricultural worker ratio on the y-axis to show their
relation in graphic form.
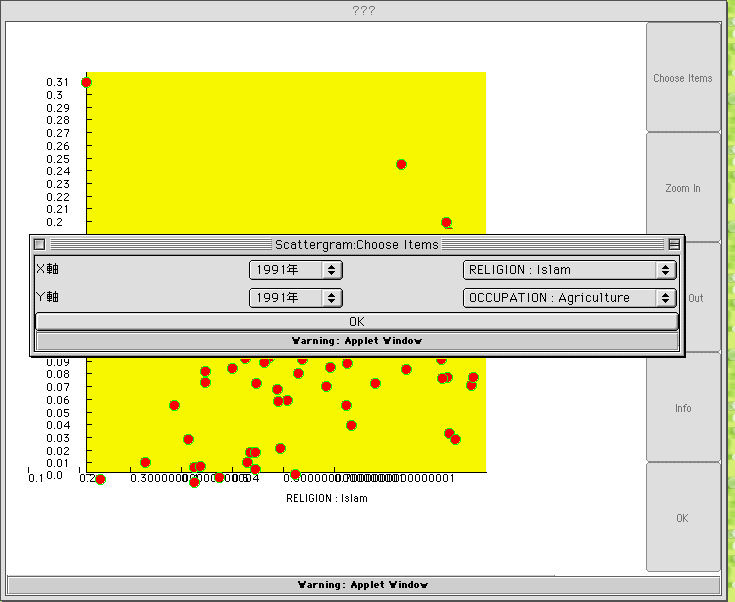
Fig. 9. Sample
scattergram.
Analysis
This function allows the
user to calculate statistics (mean, standard deviation, variance)
for selected variables. Figure 10 shows an example of Islam
ratio for all 844 mukims in Peninsular Malaysia in
which the mean is 0.738, the standard deviation is 0.258 and the
variance is 0.066.
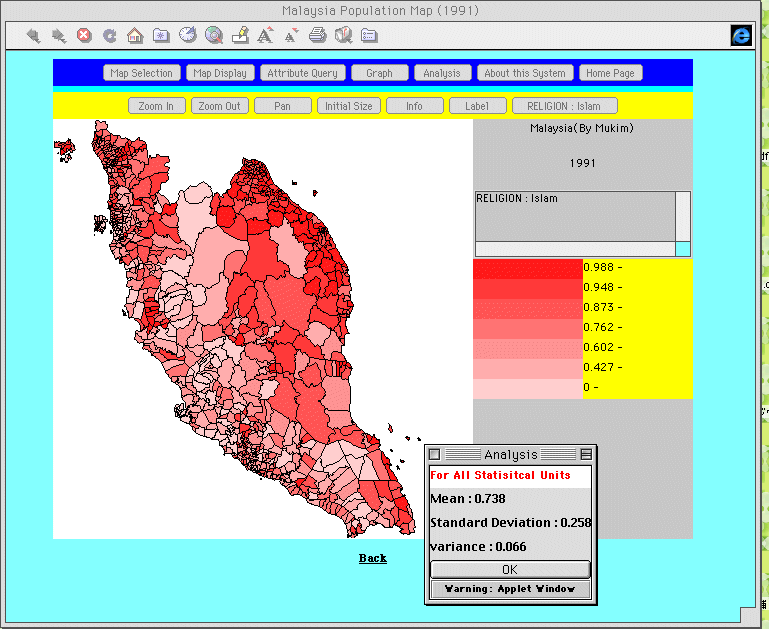
Fig. 10. Analysis
function.
This function allows
users to combine a map with a graph to find patterns,
relationships, etc. For example, clicking a point (region)
on a distribution map will make that region appear on a regular
map, while clicking a region on the regular map will make it
appear as a mark on the distribution map.
@
CONCLUDING REMARKS
The system in the present
study has been constructed with both English and Japanese
versions. This allows it to be used in Japanese classroom
education, such as in high school geography classes.
Hereafter, it will be very important to gradually expand the database by digitizing data from other years of the Population and Housing Census of Malaysia to provide a better temporal understanding of these data. In addition, it will be necessary to add spatial analytical functions to meet the high demands on Internet GIS.
@
This system, presently in the experimental stage, is accessible over the Internet at ../../index-e.html
@
I would like to express my appreciation to Mr. Hisaji Ono of the Pasco Corporation for creating this Internet GIS program.
@
1) The Census of 1991 covered all persons
including foreigners living or who were in Malaysia on Census
Day, i.e., 14 August 1991. However, Malaysian citizens and
permanent residents who were temporarily away from the country on
Census Day because of duties, touring or studying were excluded.
The 1991 Census also covered wayfarers. The category wayfarers
refer to persons who, on Census Day (between 12 midnight, 13
August 1991 and 7 a.m., 14 August 1991), were travelling along
highways or were on trains or boats (ships). Wayfarers were
included in the place in which they were found at that particular
timeiDSM, 1992.
2) Data for some regions in Peninsular
Malaysia are available from 1871, but they do not cover the
entire region. Since 1911, population censuses have been taken in
1921, 1931, 1947, 1957, 1970, 1980 and 1991. This paper looks at
only the data from 1980 and 1991, but in the future an effort
will be made to eventually create a chronological database.
3) The number of basic units used in the
present study was 642 for 1980, and 879 for 1991.
DSM (1992): Preliminary count report for urban and rural areas. Department of Statistics Malaysia,, Kuala Lumpur, p.10.
@
Murayama, Y. and H. Ono (1998): Development of Internet GIS: Map information system of regional statistics in the Meiji period. Tsukuba Studies in Human Geography, 23, 99-128.
@
Murayama, Y. (1999): Internet GIS: Map information systems of population census in 1920 and 1930. Tsukuba Studies in Human Geography, 24, 59-79.
@
Plewe, B. (1997):GIS online: information retrieval, mapping, and the internet. OnWord Press, Santa Fe, 311p.
@
@